In the tapestry of language, English grammar stands out as the intricate framework that weaves clarity, precision, and expression into our communication. Mastering these rules is not just about adhering to rigid structures but about embracing the rhythm and flow that make English a vibrant and dynamic language. This article delves into the essence of English grammar, unraveling its complexities and presenting them in a manner that enlightens and engages. Whether you’re a language enthusiast, a diligent student, or simply curious, this exploration offers valuable insights into the building blocks of effective communication in English.
Introduction to English Grammar Rules

Ah, grammar! That sometimes dreaded, often misunderstood, yet utterly essential heartbeat of language. Why bother with it, you ask? Well, imagine a world where sentences roam wild, untamed by punctuation, unstructured by syntax—a chaotic cacophony of words! Grammar is the invisible hand that brings order to this chaos, enabling us to convey our thoughts with clarity and precision.
But fear not! This journey through English grammar isn’t about memorizing a list of draconian rules. Instead, it’s about discovering the patterns that empower us to communicate effectively. From the building blocks of sentences to the nuances of verb tenses, we’ll unravel the mysteries of grammar in a way that’s engaging, insightful, and, dare I say, fun!
So buckle up! Whether you’re penning a novel, drafting an email, or simply aiming to impress at your next trivia night, a solid grasp of grammar is your trusty sidekick. Let’s embark on this linguistic adventure together, exploring the rules, recognizing common pitfalls, and uncovering the beauty of well-crafted sentences.
By the end of this article, the fog of confusion will lift, revealing a landscape where words dance with precision, and sentences resonate with clarity. Ready to dive in? Let’s get started on this exciting exploration of English grammar!
Core Grammar Concepts
Diving into the heart of English grammar, we find ourselves amidst the core concepts that are the pillars of effective communication. Understanding these foundational elements is like having a roadmap in the vast landscape of language, guiding us to express our thoughts with clarity and coherence.
Parts of Speech
At the core of English grammar lie the parts of speech, the building blocks that give sentences their structure and meaning. Let’s unravel these essential elements:
- Nouns: The names of people, places, things, or ideas—like freedom, Alice, or mountains. They’re the subjects and objects that populate our sentences, bringing them to life.
- Pronouns: These handy words, such as he, they, or ours, stand in for nouns, adding variety and preventing repetition. Imagine constantly repeating someone’s name in a conversation—tedious, right? Pronouns keep things interesting.
- Verbs: The action heroes of our sentences, verbs like run, think, or be, depict actions, states, or occurrences, driving the narrative forward.
- Adjectives: These descriptive words, such as beautiful or swift, spice up our language, adding color and detail to nouns, painting vivid pictures in the reader’s mind.
- Adverbs: Modifying verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, words like quickly or extremely refine our meaning, offering nuance and depth to our sentences.
- Prepositions: These little connectors, like in, on, or between, establish relationships in space and time, providing context that’s crucial for clarity.
- Conjunctions: The glue of language, conjunctions like and, but, or because, link words, phrases, or clauses, weaving them into coherent wholes.
- Interjections: Expressive words like Wow! or Oops! inject emotion and immediacy, adding a human touch to our utterances.
Sentence Structure
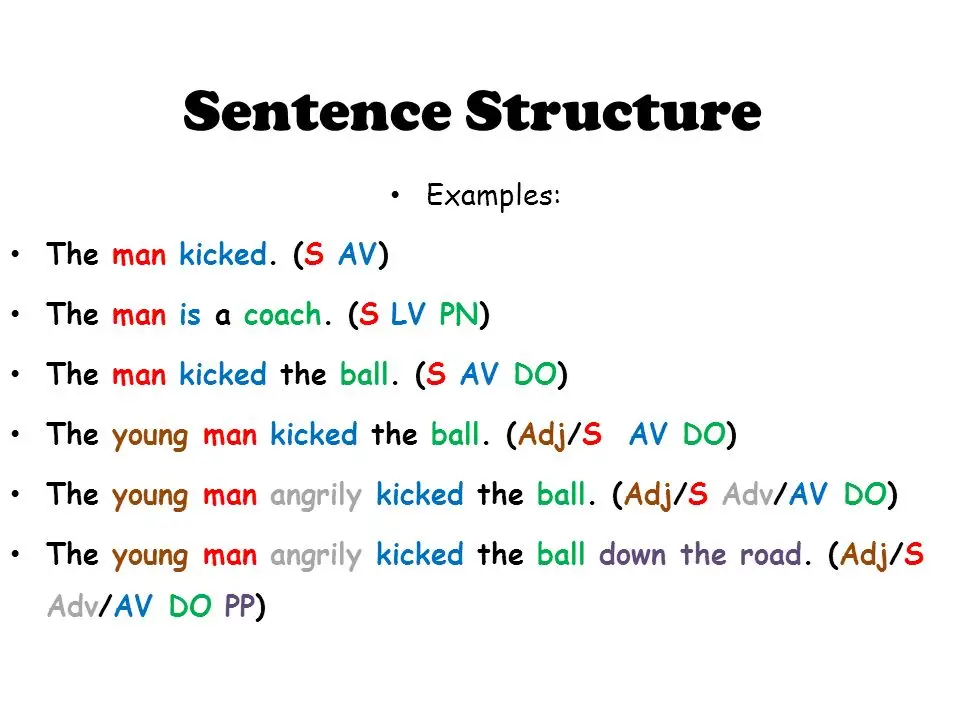
Understanding sentence structure is akin to knowing the blueprint of a building—it’s all about how the parts come together to form a stable, coherent whole.
- Subjects: The doers of the action or the focus of the sentence. It’s often a noun or pronoun, standing proudly at the sentence’s helm.
- Predicates: The part of the sentence that tells us what the subject is doing or being. It’s where the verb flexes its muscles, along with any complements or modifiers.
- Objects: These are the recipients of the action, often lounging at the end of the sentence, basking in the attention they receive from the verb.
Tenses
Tenses are the timekeepers of language, situating our actions and narratives in the past, present, or future.
- Past: Reflecting on bygone events with a nostalgic air, the past tense takes us back to moments already unfolded.
- Present: Here and now, the present tense grounds us in the current moment, where actions unfold in real-time.
- Future: Gazing into the horizon, the future tense speaks of possibilities and events yet to come, painting a picture of what may be.
Punctuation
Punctuation—the traffic signals of language—guides readers through the twists and turns of our sentences.
- Periods: The full stop, a definitive signal that one thought has concluded before another begins.
- Commas: These versatile marks, like breaths in a sentence, can separate elements, link independent clauses, or introduce items in a list.
- Semicolons: The subtle semicolon, a mediator between closely related sentences, offers a pause more significant than a comma but less final than a period.
- Colons: Introducing explanations or elaborations, colons pave the way for what follows, be it a list, a quotation, or a revelation.
By mastering these core grammar concepts, we not only refine our language but also enhance our ability to convey our thoughts and stories with precision and flair. In the next part, we’ll delve into advanced grammar rules, where complexity meets clarity, enriching our linguistic repertoire.
Advanced Grammar Rules
Venturing deeper into the realm of English grammar, we encounter advanced rules that elevate our language skills from mere competence to artistry. These nuanced elements allow for more sophisticated expression and finer control over our communication, providing the tools to convey complex ideas with elegance and precision.
Clauses and Phrases

The intricacies of English grammar reveal themselves through the interplay of clauses and phrases, the building blocks of complex sentences:
- Clauses: These are sentence fragments that contain a subject and a verb, forming the backbone of our statements. They come in two flavors:
- Independent Clauses: These can stand alone as complete sentences, carrying their own weight with a subject and a verb, like “The sun sets.”
- Dependent Clauses: These cannot stand alone and depend on an independent clause to make sense, like “when the sun sets” in the sentence “The sky turns orange when the sun sets.”
- Phrases: These are groups of words that act as a single unit in a sentence but don’t have the subject-verb pairing necessary to be a clause. For instance, “under the bed” in “The cat hid under the bed.”
Passive vs. Active Voice
The choice between passive and active voice can dramatically affect the clarity and impact of our writing:
- Active Voice: This is when the subject of the sentence performs the action, as in “The chef cooked a delicious meal.” Active voice is direct and vigorous, often making sentences clearer and more dynamic.
- Passive Voice: Here, the focus is on the action or the object of the action, rather than who is performing the action, as in “A delicious meal was cooked by the chef.” While passive voice can be useful for focusing on the action itself or when the doer is unknown or irrelevant, it can sometimes make sentences more cumbersome or less engaging.
By mastering the use of clauses, phrases, and voice, we can construct sentences that are not only grammatically correct but also rhythmically pleasing and effective in conveying our intended meaning. These advanced rules allow for nuanced expression, enabling us to paint with the full palette of the English language.
In the next section, we’ll explore common grammar mistakes and how to avoid them, helping you to refine your grammar skills further and communicate with greater confidence and precision.
Common Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Navigating the English language can sometimes feel like walking through a minefield of potential mistakes. But fear not! By becoming aware of these common errors, you can sidestep the pitfalls and enhance your writing clarity and effectiveness.
Its vs. It’s
- Its indicates possession, belonging to it: “The cat chased its tail.”
- It’s is a contraction for “it is” or “it has”: “It’s been a long day.”
Tip: If you can replace it with “it is” or “it has” and the sentence still makes sense, use it’s.
Your vs. You’re
- Your shows possession, something that belongs to you: “Is this your book?”
- You’re is a contraction for “you are”: “You’re going to love this movie.”
Tip: Substitute “you are” in the sentence. If it fits, you’re is the right choice.
There, Their, and They’re
- There refers to a place or point: “Look over there.”
- Their indicates possession, belonging to them: “Their opinions vary.”
- They’re is a contraction for “they are”: “They’re playing soccer.”
Tip: Test the sentence with “they are.” If it works, they’re is correct.
Fewer vs. Less
- Fewer refers to countable items: “She bought fewer apples.”
- Less is used with uncountable quantities: “He has less patience now.”
Tip: If you can count it, go for fewer. If not, less is your word.
Affect vs. Effect
- Affect is usually a verb, meaning to influence: “The weather can affect your mood.”
- Effect is a noun, meaning the result of a change: “The effect of the new law was immediate.”
Tip: Remember, affect is an Action, and effect is the End result.
By keeping these tips in mind, you can avoid some of the most common grammar pitfalls, making your writing more polished and professional. In the following section, we’ll delve into a collection of frequently asked questions, providing you with even more insights to hone your grammar mastery.
FAQs
In the realm of English grammar, questions abound as learners and seasoned speakers alike seek to navigate its complex landscape. Here, we address some of the most common queries, shedding light on areas that often spark curiosity or confusion
How Can I Improve My Grammar Skills?
Improving grammar is a journey of continuous learning and practice. Here are a few strategies:
- Read Regularly: Exposure to well-written material can naturally enhance your understanding of grammar.
- Practice Writing: Regular writing helps you apply grammar rules actively, solidifying your knowledge.
- Use Grammar Resources: Books, websites, and apps dedicated to English grammar can be invaluable tools.
- Seek Feedback: Getting your writing reviewed by others can highlight areas for improvement.
Why Is Grammar Important in Everyday Communication?
Grammar is the backbone of effective communication. It ensures that your message is conveyed clearly and correctly, preventing misunderstandings. In professional settings, good grammar reflects credibility and attention to detail.
Can I Use Contractions in Formal Writing?
While contractions are common in informal writing and speech, they are generally avoided in formal writing. They can make the text seem less serious or professional. However, the rules are becoming more flexible, and some contractions are becoming acceptable in less stringent formal contexts.
Is Ending a Sentence with a Preposition Acceptable?
The rule against ending sentences with prepositions is a remnant of Latin grammar rules applied to English. Modern English usage experts agree that ending sentences with prepositions is acceptable, particularly when it makes the sentence sound more natural and the meaning more clear. Interestingly, this practice was once considered a grammatical taboo. Nonetheless, contemporary linguists advocate for clarity and natural flow in writing, thereby supporting this flexible approach. Consequently, while adhering to traditional rules, it’s equally important to prioritize the reader’s understanding and the overall coherence of the sentence.
Conclusion: Embracing the Journey of Grammar Mastery
Embarking on the journey of grammar mastery is akin to setting sail on the vast seas of language. Along the way, we encounter waves of complexity and islands of nuance, each exploration enhancing our ability to navigate the world of communication with greater finesse and confidence.
As we’ve journeyed through the foundational pillars of English grammar, delved into advanced rules, sidestepped common pitfalls, and answered pressing questions, we’ve equipped ourselves with the tools to craft sentences that resonate with clarity and elegance. Grammar, far from being a mere set of rigid rules, is a living, breathing aspect of language that evolves with us, shaping our thoughts and reflections.
In every noun’s steadfast presence, every verb’s dynamic action, and every adjective’s descriptive flourish, we find the essence of expression—a means to share our stories, convey our ideas, and connect with others across the expanse of human experience. By embracing grammar’s guiding principles, we unlock the potential to transform our words into powerful vessels of meaning, navigating the nuanced realms of language with skill and grace.
As you navigate English grammar’s complexities, remember every step and learned rule enhances communication. Let curiosity, persistence, and discovery guide your journey. Use grammar to craft your unique narrative.

